Microwave Engineering (ÃÊ°íÁÖÆÄ°øÇÐ)
1. °øÁö»çÇ×
¤· Grading: Ãâ¼® 15% (°úÁ¦Á¦Ãâ·Î È®ÀÎ), °úÁ¦ 15%, Áß°£½ÃÇè 35%, ±â¸»½ÃÇè 35%
¤· Textbook:
- ¿ø¼: D. M. Pozar, Microwave Engineering, 4th Ed., Wiley, 2015.
- ¹ø¿ª¼: ¸¶ÀÌÅ©·ÎÆÄ°øÇÐ (D. M. Pozar Àú), °íÁöȯ ¿ª, ÇÑƼ¿¡µà, 2020.
¤· °úÁ¦¿ë Çлý°íÀ¯¹øÈ£ PIN: Çб³¿¡ µî·ÏµÈ ÀÚ½ÅÀÇ À̵¿ÀüÈ ³¡ 4ÀÚ¸®. ´Ü °¢ ¼ýÀÚ°¡ 0ÀÎ °æ¿ì ¼øÂ÷ÀûÀ¸·Î 1, 2, 3, 4·Î ´ëü. ¿¹½Ã: 4321 ¡æ 4321, 4010 ¡æ 4112
¤· °úÁ¦ Á¦Ãâ: eCampus¿¡ ¾÷·Îµå. ´ÙÀ½ ÁÖ ¼ö¾÷ÀÏ 23:59±îÁö. ¼ö±â´ä¾È ÃÔ¿µÇÏ¿© ¾÷·Îµå
¤· ½Ç½À°á°ú Á¦Ãâ: eCampus¿¡ ¾÷·Îµå. ´ë¸éÇлý=¼ö¾÷½Ã°£ ³», ºñ´ë¸éÇлý=´ÙÀ½ ÁÖ ¼ö¾÷ÀÏ 23:59±îÁö. ¼Ò½ºÄÚµå¿Í ÄÚµå½ÇÇà °á°ú¸¦
MS¿öµå¹®¼(*.doc, *.docx)·Î ¸¸µé¾î ¾÷·Îµå
¤· °ÀÇ½Ç ¼ö¿ëÀοø ÃÊ°ú¿Í Covid-19 È®»ê¹æÁö¸¦ À§ÇØ 3±×·ìÀ¸·Î ³ª´©¾î °¢ ±×·ìº° 4ÁÖ¾¿ ´ë¸é ¼ö¾÷. ±×·³¿¡µµ ¸ðµÎ ´ë¸é¼ö¾÷À¸·Î °øºÎÇÏ°íÀÚ ÇÏ´Â ÇлýÀº °ÀÇ½Ç Ãâ¼®ÇÒ ¼ö ÀÖÀ½.
1±×·ì(1-4ÁÖ): À̱â*(2Çгâ), °±æ* to ¹ÚÀç* (3Çгâ 20¸í)
2±×·ì(5,6,7,9ÁÖ): ¹è¿µ* to Àü´Ù* (3Çгâ 20¸í)
3±×·ì(10-13ÁÖ): * Bin, Á¤Âù* to ȲÁö* (3Çгâ), 4Çг⠱谡*, ±èÅÂ*, ¹Ú°æ*, ¼Õ¿¹*, ¾ç¿ì*, À±Á¤*, ÀÌ°æ*, ÀÌ»ó*, ÀÌÇý* (21¸í)
¤· °ÀÇ°ü·Ã ¹®ÀÇ»çÇ×: ´ã´ç±³¼ö bician@cbu.ac.kr (E10-611)
½Ç½ÀÁ¶±³ ¸ð³×ºñ aydjmonebitee@gmail.com (E10-519) (2ÁÖ-15ÁÖ), ÇãÁö¿ø ÇãÁö¿ø gjwldnjs131@naver.com (E10-519) (1ÁÖ)
äÁ¡Á¶±³ ÃÖ°æ¹Î ckm45@naver.com
2. ÁÖº° °ÀÇ
Week-01(3/4):
Transmission Lines 1
ÀÌ·Ð: °ÀÇ(pdf, pptx-no-voice, pptx-voice, mp4)
½Ç½À: °ÀÇÀÚ·á(pdf, htm), À½¼º°ÀÇ(ÆÄÀ̽ã»ç¿ë¹ý&½Ç½À3¹ø, ½Ç½À1¹ø&2¹ø, ½Ç½À4¹ø)
(Homework 01)
1. Express the characteristic impedance Z0 of a transmission line in
terms of R, L, G, and C.
2. Express the complex propagation constant ¥ã of a
transmission line in terms of R, L, G,
and C.
3. Express Z0
and ¥ã of a lossless transmission line
in terms of L and C.
4. Write down a Python program and execute it to
find the characteristic impedance Z0
and the complex propagation constant ¥ã
of a transmission line with R = 176 m¥Ø/m, L = 490 nH/m, G = 2 ¥ìS/m, C = 49 pF/m. Accept the frequency f while the code runs as an input data
of your choice.
Week-02(3/11):
Transmission Lines 2
ÀÌ·Ð: °ÀÇ(pdf, pptx-no-voce, pptx-voice, mp4)
½Ç½À: °ÀÇÀÚ·á(pdf, htm), À½¼º°ÀÇ(mp4)
(Âü°í) °úÁ¦¹®Á¦ Ç®¶§ ÇÊ¿äÇÏ¸é ´ÙÀ½ÀÇ º¹¼Ò¼ö °è»ê±â »ç¿ë
º¹¼Ò¼ö °è»ê±â: Á÷°¢ÁÂÇ¥/±ØÁÂÇ¥ Çü½Ä º¯È¯, °ö¼À, »¬¼À
Python:
complex_calc_1_python.txt
Fortran:
complex_calc_1.f90, complex_calc_1.exe
(Homework 02)
PIN=pqrs,
a = p+q+r+s, b = 3*a
Coaxial cable with a(given above), b(given
above), ¥ìr = 1, ¥år
= 2, tan¥ä = 0.001, ¥ò = 5.8e7 S/m, f = 5.8 GHz
Calculate Z0,
¥ã, R, L, G, C,
¥ác (dB/m), ¥ád (dB/m), ¥á (dB/m), ¥ëg.
(Âü°í) ´ÙÀ½ °ø½Ä »ç¿ë
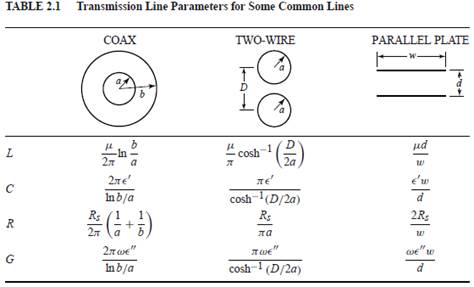
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Week-03(3/18):
Transmission Lines 3
ÀÌ·Ð: °ÀÇ(pdf, pptx-no-voice, pptx-voice, mp4)
½Ç½À: °ÀÇÀÚ·á(pdf, htm), À½¼º°ÀÇ(mp4)
(Homework 03)
Visit http://mcalc.sourceforge.net/ to analyze a microstrip line.
´ÙÀ½°ú °°ÀÌ ¼³Á¤
´ÜÀ§¸¦ mm ¼³Á¤
Er
= 4.3, Rho =1
H
= 1, Rough = 0.0
Tmet
= 0.035, Tan¥ä = 0.02
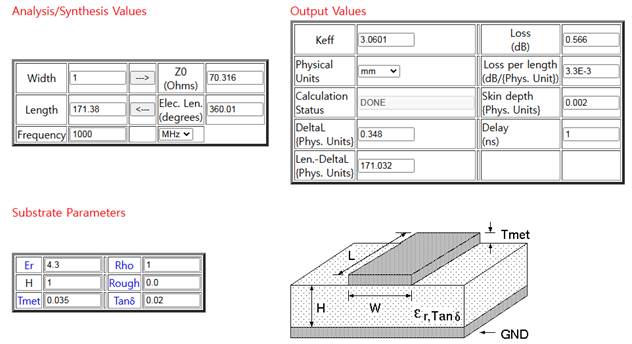
Keff´Â ¥åre (À¯È¿ À¯Àü»ó¼ö)
¼±·ÎÆÄÀå:
![]()
Elec. Len. (degrees) = ¼±·ÎÀÇ Àü±âÀû ±æÀ̸¦ °¢µµ·Î Ç¥Çö. 1ÆÄÀåÀº 360¡Æ¿¡ ´ëÀÀµÈ´Ù.
(¹®Á¦)
W = 2mm, Frequency = 1500MHz ÀÎ °æ¿ì Z0, Keff, L (1ÆÄÀåÀÇ ±æÀÌ)¸¦ ±¸Ç϶ó. ÀÌ °æ¿ì Loss (dB)¸¦ ±¸Ç϶ó.
Week-04(3/25):
Smith Chart
ÀÌ·Ð: °ÀÇ (pdf, pptx-no-voice, pptx-voice, mp4)
½Ç½À: °ÀÇÀÚ·á(pdf, htm), À½¼º°ÀÇ(mp4)
Âü°í: Smith-z-chart, Smith-y-chart, Smith-zy-chart
(Homework 04)
PIN=abcd (PIN=3194, a=3, b=1, c=9,
d=4)
1. Draw a r = a circle on a Smith
chart.
2. Draw a x = d circle on a Smith
chart.
Wee-05(4/1):
Impedance Matching 1
ÀÌ·Ð: °ÀÇ (pdf, pptx-no-voice, pptx-voice, mp4)
½Ç½À: °ÀÇÀÚ·á(pdf, htm), À½¼º°ÀÇ(mp4)
(Homework 05) PIN=abcd (exmple: PIN=3194, a=3, b=1,
c=9, d=4)
Vs = 10a ¡¿ exp(j20¡Æ)
Zs = 10b + j 10c (ohm) : connected in series with
Vs
ZL = 30a − j 40d (ohm) : connected in series with
Zs
1. Find the power PL (W) at ZL
2. Modify ZL for maximum power transfer.
3. Find the power PL (W) at ZL when ZL is modified
for the maximum power transfer.
Week-06(4/8):
Impedance Matching 2
ÀÌ·Ð: °ÀÇ (pdf, pptx-no-voice, pptx-voice, mp4)
½Ç½À: °ÀÇÀÚ·á(pdf, htm), À½¼º°ÀÇ(mp4)
(Âü°í) LC matching: Python souce code (python-general LC matching.doc)
(Homework 06) PIN=abcd (exmple: PIN=3194, a=3, b=1,
c=9, d=4)
1. Find all the possible element values of LC-matching networks that transforms
10a+j40b ¥Ø to 50 ¥Ø. Use the Python
code given above.
Week-07(4/15):
Passive RLC Components 1 - Resistors
ÀÌ·Ð: °ÀÇ (pdf, pptx-no-voice, pptx-voice, mp4) (À½¼º°ÀÇÀÚ·á´Â ÀÛ¾÷ÁßÀÌ¸ç ±ÝÀÏÁß ¾÷·ÎµåµË´Ï´Ù.)
½Ç½À: °ÀÇÀÚ·á(pdf, htm), À½¼º°ÀÇ(mp4)
(Homework 07) PIN=abcd (exmple: PIN=3194, a=3, b=1,
c=9, d=4)
1. Resistor equivalent circuit
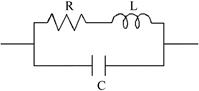
1) Find an expression for the impedance.
2) f = a MHz, R = 100b (ohm), L = b nH, C= 2d pF.
Calculate the impedance.
Week-08(4/22):
Mid-term Exam. (prob, sol): ´ä¾ÈÀº
eCampus 8ÁÖÂ÷ °úÁ¦¶õ¿¡ Á¦Ãâ
Áß°£°í»ç: ¹®Á¦(pdf, htm)
Week-09(4/29):
Passive RLC Components 2 - Capacitors
ÀÌ·Ð: °ÀÇ (pdf, pptx-no-voice, pptx-voice, mp4)
½Ç½À: °ÀÇÀÚ·á(pdf, htm), À½¼º°ÀÇ(mp4)
½Ç½À: ¹®Á¦(pdf, htm), ÇØ´ä(pdf)
(Homework 09) PIN=abcd (exmple: PIN=3194, a=3, b=1,
c=9, d=4)
1. Capacitor equivalent circuit
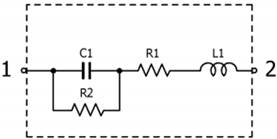
1) Find and expression for the impedance.
2) f = 100a MHz, C1 = 20b nF, R2=b Gohm, R1=c/100
ohm, L1 = d/4 nH. Calculate the impedance.
Week-10(5/6):
Passive RLC Components 3 - Inductors
ÀÌ·Ð: °ÀÇ (pdf, pptx-no-voice, pptx-voice, mp4)
½Ç½À: °ÀÇÀÚ·á(pdf, htm), À½¼º°ÀÇ(mp4)
½Ç½À: ¹®Á¦(pdf, htm), ÇØ´ä(pdf)
(Homework 10) PIN=abcd (exmple: PIN=3194, a=3, b=1,
c=9, d=4)
1. Inductor equivalent circuit
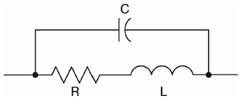
1) Find and expression for the impedance.
2) f = 100a MHz, R=10b ohm, L = 5b ¥ìH, C = d/10 pF. Calculate the
impedance.
Week-11(5/13):
Maxwell's Equations and Wave Equation
ÀÌ·Ð: °ÀÇ (pdf, pptx-no-voice, pptx-voice, mp4)
½Ç½À: °ÀÇÀÚ·á(pdf, htm), À½¼º°ÀÇ(mp4)
½Ç½À: ¹®Á¦(pdf, htm), ÇØ´ä(pdf)
(Homework 11) PIN=abcd (exmple: PIN=3194, a=3, b=1,
c=9, d=4)
1. f = 1 GHz, ¥år = a, ¥ìr
= b. Find the wavelength and the intrinsic impedance.
Week-12(5/20):
Planewave 1
ÀÌ·Ð: °ÀÇ (pdf, pptx-no-voice, pptx-voice, mp4)
½Ç½À: °ÀÇÀÚ·á(pdf, htm), À½¼º°ÀÇ(mp4)
½Ç½À: ¹®Á¦(pdf, htm) ÇØ´ä(pdf)
(Homework 12) PIN=abcd (exmple: PIN=3194, a=3, b=1,
c=9, d=4)
1. Planewave in lossy media
¥å'/ ¥å0 = a, ¥å'' =
0.1¥å', ¥ì'/ ¥ì0 = d, ¥ì''= 0, f = c GHz
Find the attenuation constant ¥á,
propagation constant ¥â, and skin
depth ¥äs.
Week-13(5/27):
Planewave 2
ÀÌ·Ð: °ÀÇ (pdf, pptx-no-voice, pptx-voice, mp4)
½Ç½À: °ÀÇÀÚ·á(pdf, htm), À½¼º°ÀÇ(mp4)
½Ç½À: ¹®Á¦(pdf, htm) ÇØ´ä(pdf)
(Homework 13)
Medium 1: air, Mediumk 2: ¥år = a, ¥ìr = b
1. Find the intrinsic impedance of the air ¥ç1 and
of the earth ¥ç2.
2. Find the reflection cofficient ¥Ã and transmission coefficient ¥ó
of a planewave normally incident from the air to the medium 2.
Week-14(6/3):
Student Self-study Week
±ÝÁÖ´Â ±â¸»°í»ç °ÀǾøÀÌ Çлý ÀÚÀ²ÀûÀ¸·Î ¹®Á¦Ç®ÀÌÇÕ´Ï´Ù.
Homework weeks 9-13 solutions
Python lab. problems weeks 9-13 solutions
Week-15(6/10):
Final exam. (prob, sol)
´ä¾ÈÀº
eCampus 15ÁÖÂ÷ °úÁ¦¶õ¿¡ Á¦Ãâ
±â¸»½ÃÇè: ¹®Á¦(pdf, htm)
[Summary of Formulas]
Lecure 01: Transmission lines 1
- Voltage and current waves
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
- R, L, G, C from Z0 and ¥ã
![]()
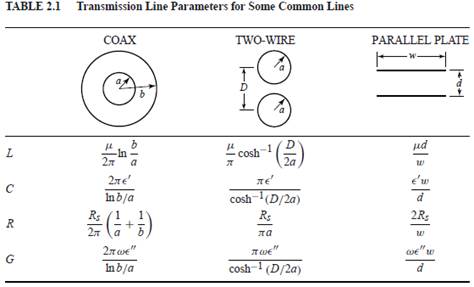
- Formulas for coaxial cable, two-wire line, and parallel-plate line
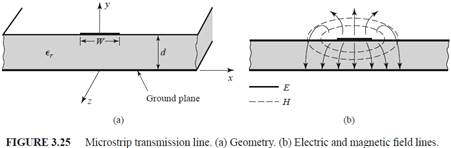
- Microstrip line formulas
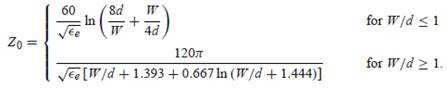
![]()
![]()