실습-08 필터(Filter)
RWG
post filter
http://www.allenavionics.com/NewProducts/Microwave/CPWB.htm
http://www.mig-germany.com/seite18.html
Matthaei,
Microwave Filters, Impedance-Matching
Networks, and Coupling Strutures, Artech House, 1980.
Hunter,
Theory and Design of Microwave Filters,
IET, 2001.
Natarajan,
A Practical Design of Lumped, Semi-Lumped
and Microwave Cavity Filters, Springer, 2012.
Jarry,
Advanced Design Techniques and
Realization of Microwave and RF Filters, Wiley/IEEE, 2008.
AMW,
Practical Filters and Couplers: A
Collection from Applied Microwave & Wireless, Noble, 2001.
Makimoto,
Microwave Resonators and Filters for
Wireless Communication: Theory, Design and Application, Springer, 2001.
Hashimoto,
RF Bulk Acoustic Wave Filters for
Communications, Artech House, 2009.
Matsumoto, Microwave Filters and Circuits: Advances
in Microwaves, Volume 1, Academic, 1970.
Aatre,
Network Theory and Filter Design, 2nd Ed.,
New Age International, 1987.
Hong,
Microstrip Filters for RF/Microwave
Applications, Wiley, 2004.
Parmanick,
Modern RF and Microwave Filter Design,
Artech House, 2016.
Rhea,
HF Filter Design and Computer Simulation,
Noble, 1994.
Rhea,
Filter Synthesis Using Genesys S/Filter,
Artech House, 2014.
Vizmuller,
Filters with Helical and Folded Helical
Resonators, Artech House, 1987.
Levy,
Classic Works in RF Engineering, Volume
2: Microwave and RF Filters, Artech House, 2007.
Verdú,
Microwave/RF Filters Based on Bulk
Acoustic Wave Resonators: Fundamentals, Design, and Applications, Lambert,
2011.
Cameron,
Microwave Filters for Communication
Systems: Fundamentals, Design and Applications, Wiley, 2007.
Zhu,
Microwave Bandpass Filters for Wideband
Communications, Wiley, 2012.
Martín,
Balanced Microwave Filters, Wiley,
2018.
Malherbe,
Microwave Transmission Line Filters,
Artech House, 1979.
Baral,
Microstrip Filters for RF/Microwave
Applications: Design, Analysis and Implementation, Lambert, 2010.
Oldoni,
Synthesis and Modelling Techniques for
Microwave Filters and Diplexers: Advances in Analytical Methods with
Applications to Design and Turning, Scholars' Press, 2014.
Budimir,
Generalized Filter Design by Computer
Optimization, Artech House, 1998.
Ozenbaugh,
EMI Filter Design, 3rd Ed., CRC,
2011.
Morgan,
Reflectionless Filters, Artech House,
2017.
Crnojević-Bengin, Advances in Multi-Band Microstrip Filters,
CUP, 2015.
Ahmed,
Optimizing the Performance of Microstrip
Filters: Microstrip and Metamaterial Microwave Filters, Lambert, 2012.
Doumanis,
Filter Design for Satellite
Communications: Helical Resonator Technology, Artech, 2014.
Helszajn,
YIG Resonators and Filters, Wiley,
1985.
Al-Sharif,
Microwave Filter Design by Continuously
Varying Transmission Line, Lambert, 2013.
Rangaiah,
Advanced Design Propelled Strategies of
the Microwave Filters: Printed Microstrip Filter Using X-Models, Lambert,
2017.
Young,
Microwave Filters Using Parallel Coupled
Lines, Artech, 1972.
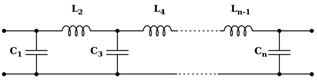
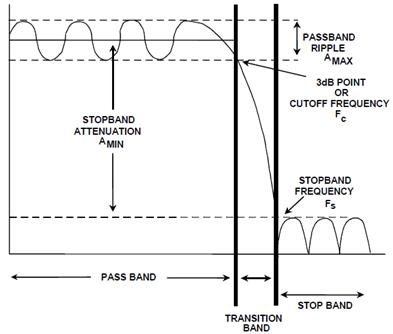
8.1 Periodic Structures
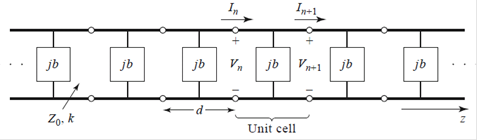
Unit
cell:
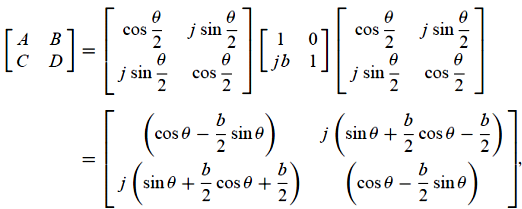

k :
propagation constant of the unloaded line
Two solutions:
![]() : propagation (pass band)
: propagation (pass band)
![]() : attenuation (stop band)
: attenuation (stop band)
Bloch wave: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bloch_wave
Bloch wave MoM method
Periodic boundary conditon
[Filter]
- 원하는 주파수 성분만 통과 또는 차단
- 용도: 신호간섭 피해 방지, 간섭신호 발생 방지
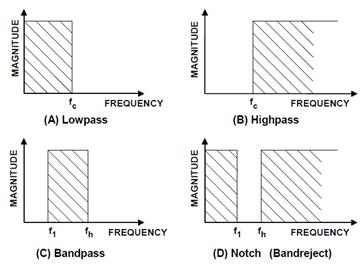
- 종류:
저역통과필터(LPF)
고역통과필터(HPF)
대역통과필터(BPF)
대역저지필터(BSF)
- 특수 필터
다중 대역통과필터
멀티플렉서
[Filter types]
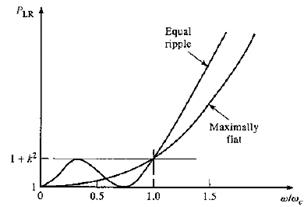
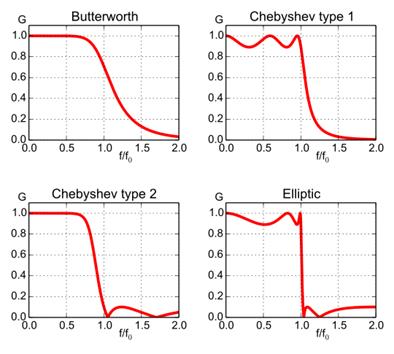
Butterworth
filter
Chebyshev
filter
Elliptic
(Cauer) filter
Bessel
filter: maximally flat linear phase response, preserves the signal shape
Gaussian
filter
Optimum
"L" (Legendre) filter
Linkwitz-Riley
filter
Image
impedanc filter
[Filter
response function shape]
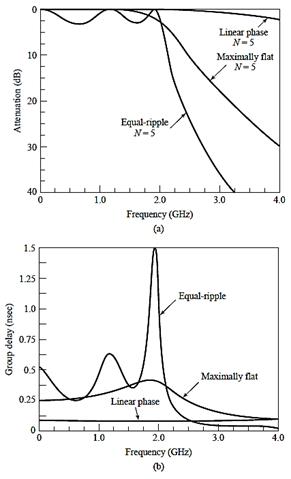
[Group delay]
-
Derivative of the phase with respect to angular frequency
- A
measure of the distortion in the signal
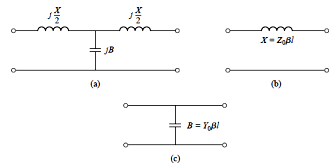
[LC filter]
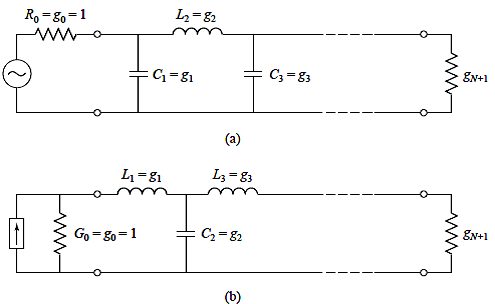
1.
Butterworth filter
![]()
g0: source resistance or conductance
gN+1: load resistance (if gN is a shunt capacitor) or load conductance (if gN is a series capacitor)
Pozar:
Table 8.3
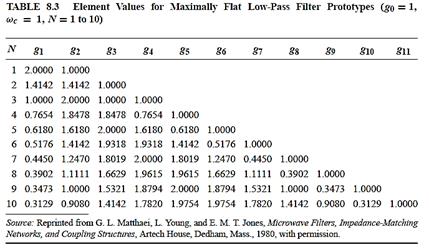
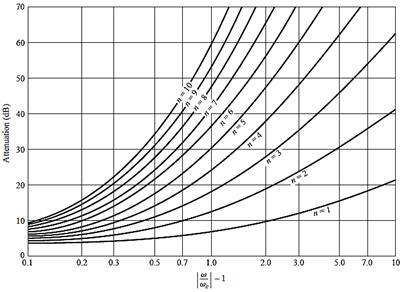
2.
Equi-ripple filter = Chebyshev filter
Pozar:
Table 8.4
3.
Linear phase response = maximally flat time-delay = maximally flat group-delay
Pozar:
Table 8.5
[Filter
Transformation]
1.
Impedanc and frequency scaling

2.
Filter type transformation
![]()
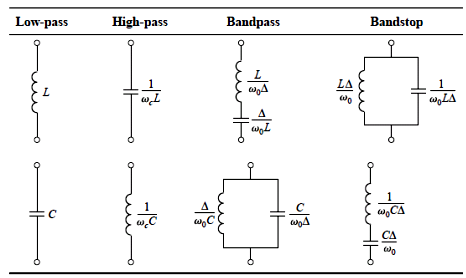
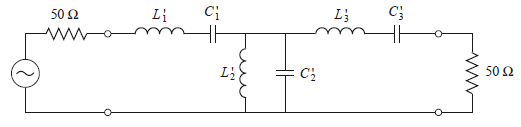
Design
example:
0.5-dB
equi-ripple
N = 3
fc = 1GHz
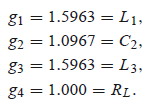
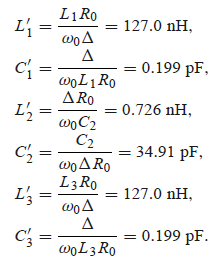
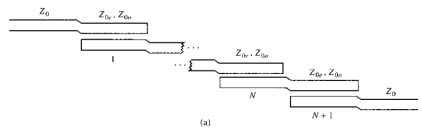
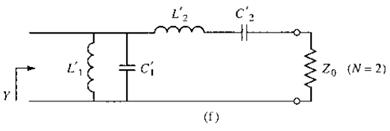
[Microstrip
filter]
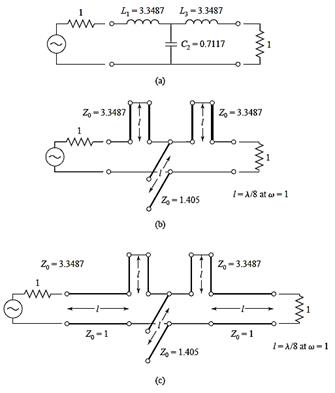
1.
Stub-loaded low-pass filter
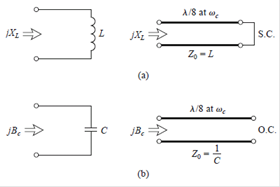
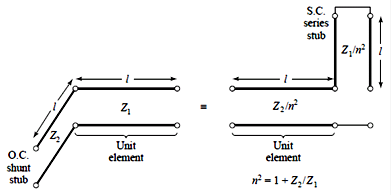
Design
example: 3-dB equi-ripple, LPF, 3GHz, 50Ω
2.
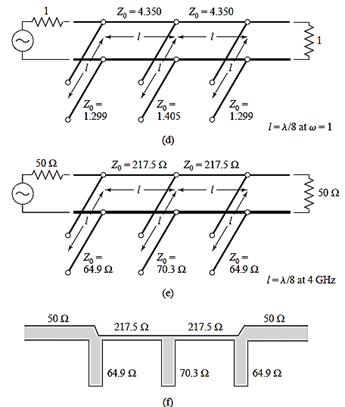
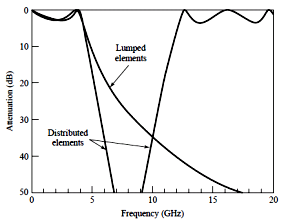
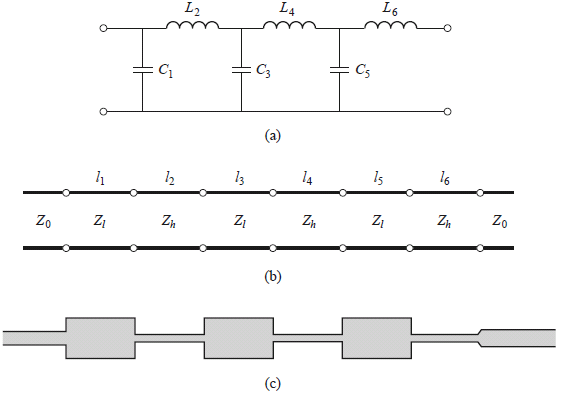
Stepped impedance LPF
![]()
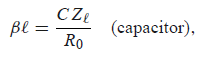
Design
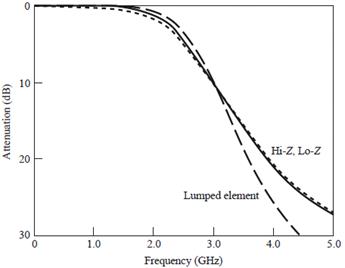
example: maximally flat, fc
2.5GHz, 20dB insertion loss at 4GHz, 50Ω
microstrip
impedance range: 20-120Ω
er
=4.2, tand = 0.01, 0.5-mil substrate
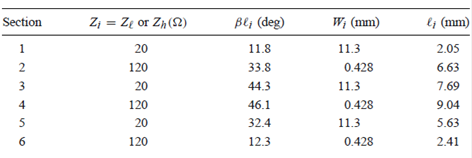
N = 6 from attenuation requirement
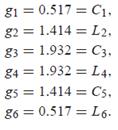
3.
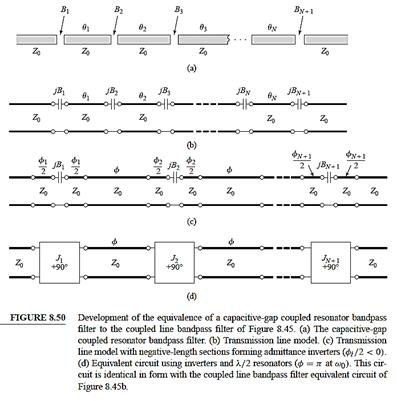
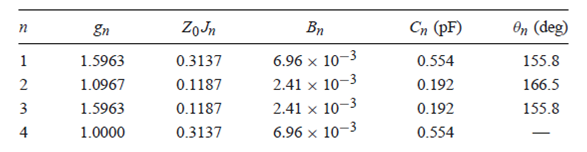
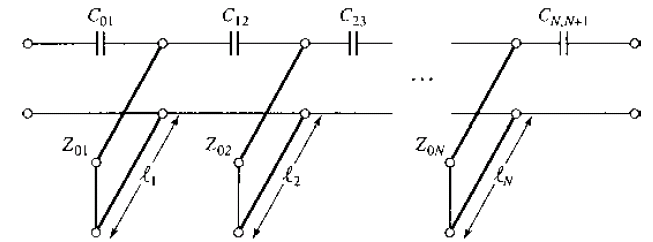
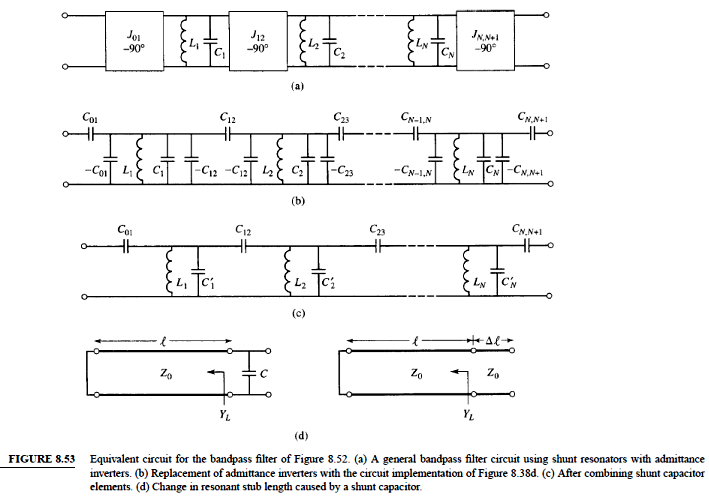
Coupled-line BPF
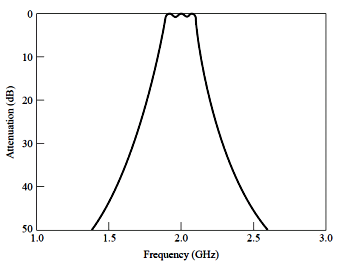
Coupled-resonator
filters
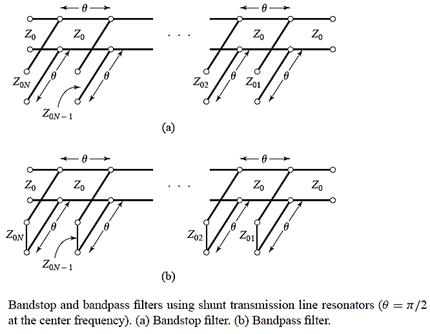
Design
example:
Capacitively-coupled
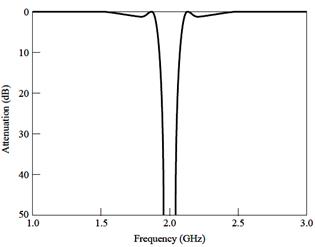
series resonator BPF
Degisn
example: 2.0GHz, 0.5dB equi-ripple, 10%, 20dB at 2.2GHz
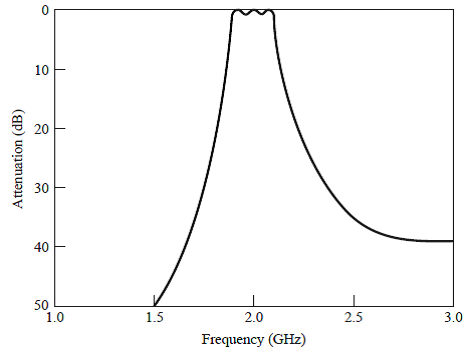
BPF using
capacitively-coupled shunt resonators
[Keywords]
immitance:
normalized impedance or admittance, normalized (so it is unitless)
prototype
filter: ![]()
filter
transformation: frequency scaling, impedance scaling, type transformation
[Rational
function respresentation of the filter transmission function]
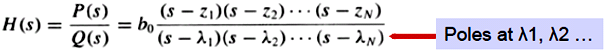
poles
zeros
transfer
function
complex
frequency: ![]()
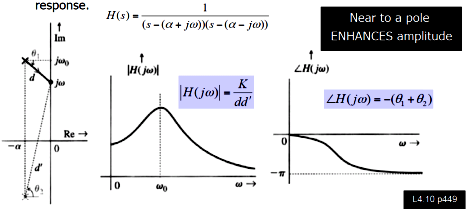
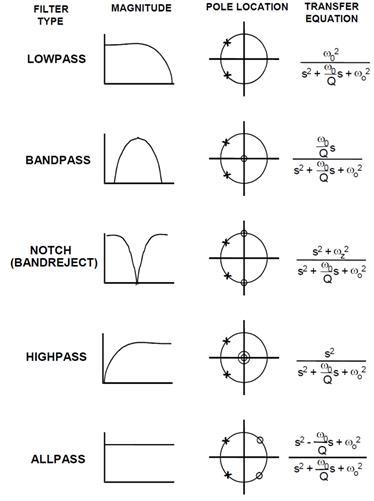
Bandpass
filter poles:
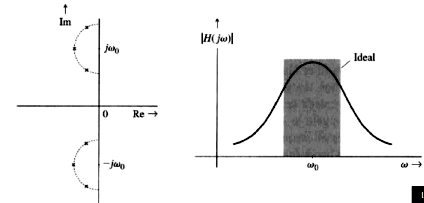
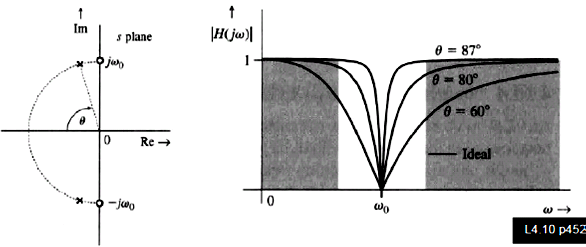
Notch
filter: a pole close to a zero makes the gain near unity at zero and infinite
frequency.
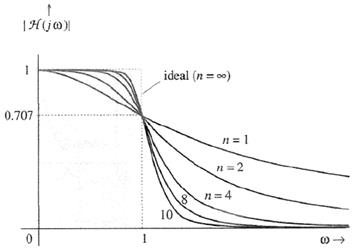
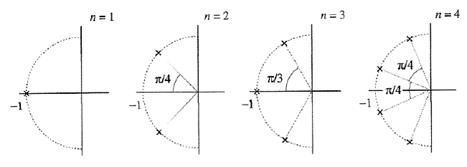
Butterworth
filter:
![]()
![]()
]
[Filter
implementation
1.
Digital implementation
-
Bilinear transform method
-
The matched z-transform method
-
For higher orders, digital filters are sensitive to quatization errors
2.
Sallen-Key topology: uses active and passive components
Example:
second-order Butterworth filter
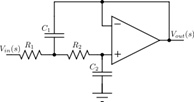
3.
Cauer topology: uses passive components