Radar
Applications
I. List
of Radar Applications
1. Radars
for Civil Applications
Proximity sensor,
intruder detector, firearm detection airport security radar
Speed meter, police
radar
Ground penetrating
radar, through-wall radar, bridge inspection radar
Altimeter radar:
commercial aircrafts
Level sensor:
chemical plant
Automotive radar: 24 GHz,
77 GHz, anti-collision radar, lane proixmity warning
Air traffic control
radar
Radio astronomy
radar, planetary radar
Shipboard radar:
navigation (collision avoidance), military
Airborne radar: weather
radar, collision avoidance, ground imaging
Satellite radar:
ground imaging, remote sensing
Spacecraft radar: Venus
radar mapper
2. Radars
for Military Applications
Altimetry: missile
navigation
Surveillance: personnel
detection, coastal defense, ground defense, airspace defense,
artillery locator
Guidance and attack:
missile guidance, missile seeker
Telemetry and
command: missile telemetry & command
High-resolution ground
imaging radar: aircraft radar, satellite radar
II. Radars
by Application
1. Automotive Radars


Figure: Left = Autoliv's 24-GHz radar for blind spot detection, Right = Autoliv's 77-GHz collision avoidance radar
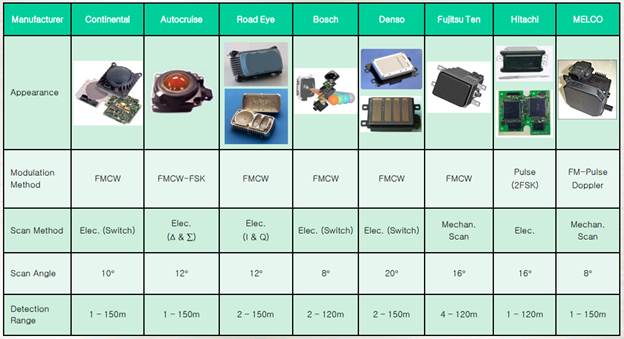
2.
Weather Radars
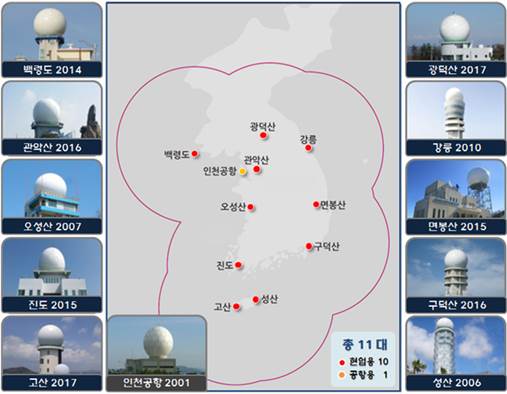
Figure: South Korean weather radar network


Figure: Weather radar on Gooduck mountain, South Korea

Figure: Rain rate measurement by a weather radar
3. Airport
Surveillance Radars, Air Traffic Control Radars

Figure: ASR-9 air traffic control radar. Curved reflector on the bottom: PSR (primary surveillance radar), flat antenn on top: SSR (secondary surveillance radar)

Figure: Monitor screen of an air traffic control radar
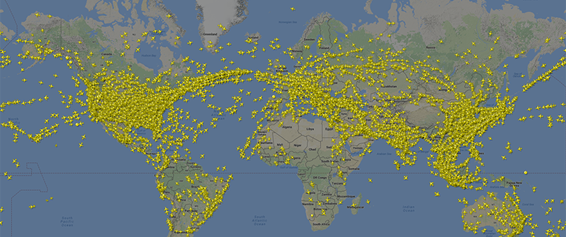
Figure: Smartphone application program for real-time view of commercial aircrafts flying all over the world.
4. Marine Navigational
Radars


Figure: Left = Sea Hawk marine radar with a 12' antenna; Right = HD or broadband radar by SIMRAD
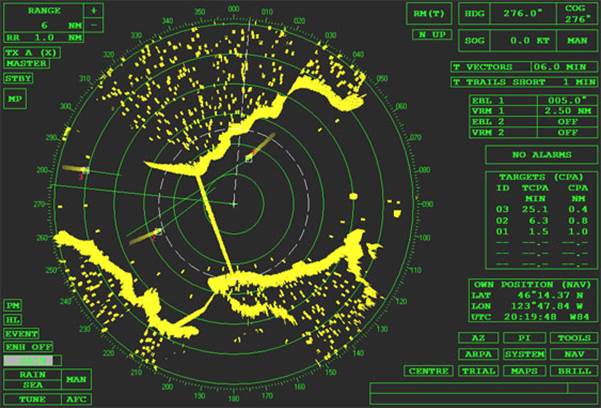
Figure: Display screen of a marine radar
5. Missile
Seeker Radars


Figure: Left = Missile fired from a ship. Right = Legacy missile radar
6. Aircraft
Radars


Figure: Left = Multi-funcion radar on a fighter aircraft, Right = Collision avoidance radar on a commercial aircraft.
7. Artillery
Locating Radars

Figure: Euro-Art COBRA (Counter Battery Radar) radar with an active electronically scanned array (AESA)
8. Missile Defense Radars


Figure: Left = Ground-based missile defense radar (THAAD), Right = AN/SPY-6 radar under test
9. Spaceborne Imaging Radars

Figure: ESA Sentinel-1 spaceborne C-band synthetic-aperture radar
10. Spacecraft
Radars

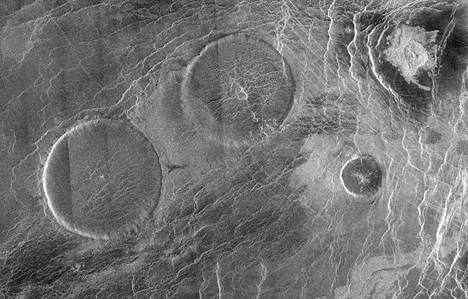
Figure: Left = Magellan spacecraft with its synthetic aperture radar (SAR) antenna on Space Shuttle STS-30 (4 May 1989), Right = SAR image of Carmenta Fara ("pancake volcanoes")