전파광파소자
실습-11 조명기술
어두운 공간을 빛으로 밝히는 조명기술은 사람의 가정생활과 사회생활에 매우 중요하다. 전기를 사용하는 현대인들은 조명을 당연한 것으로 받아 들인다. 그러자 지금도 전기가 없는 곳에서는 밤에 나뭇불, 석유등, 가스등을 사용하여 어둠을 밝혀야 한다.
가정용과 상업용 조명으로 백열등(incandesent light), 형광등(flourescent light), 소형 형광등(CFL), LED 등이 사용되고 있으며 거리와 건물 조명에는 할로겐(sodium lamp, mercury halide lamp) 등이 사용되고 있다.
조명이 필요한 기술 분야로서 컴퓨터 장치 조명(컴퓨터 모니터, 휴대기기 디스플레이), 가정 생활공간 조명(residential lighting), 상업적 조명(호텔 객실, 커피점, 대형마트), 건축조명(문화재, 도시 고층건물, 교량), 광고용 조명(상점 간판, 상품 광고판), 거리 조명(도로, 캠퍼스, 공원), 경광등(철탑, 고층건물, 항공기), 교차로 신호등, 자동차 헤드라이트 등 다양하다. 조명 분야 요소 기술로는 광원(전구), 전원 공급장치, 렌즈, 조명 fixture, 조명의 미학적 설계 등이 있다.
본 실습에서는 조명기술의 기초를 학습하고 LED 전원회로를 PSpice로 실습한다.
I. 실습
(주의 사항)
-
PSpice 회로도: 선 모두 흑색
-
PSpice 파형: 그래프 선을 두껍게 하여 잘 보이게 함.
ㅇ PSpice LED 모델
-
PSpice에서 LED library를 제공하지 않으므로 전압원과 직렬연결되 정류 다이오드를 사용
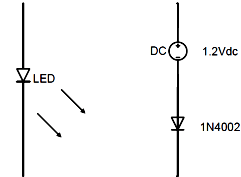
그림: LED의 PSpice 모델. LED의 순방향 전압이 1.8V인 경우
1. 230VAC LED Driver Circuit
- 아래 회로를 PSpice로 시뮬레이션 하라.
-
Red LED를 위 그림에서와 같이 1.2Vdc 전원과 1N4002 다이오드의 직렬회로로 대체

그림: 230VAC 전원을 이용한 LED 드라이버 회로 [Electronics Hub]. 2.2uF
polyester film cap 225J 400V; 390kΩ 1/4W; 10Ω 1/4W; Bridge
rectifier W10M; 22kΩ 5W; 4.7uF cap 400V, polarized; 10kΩ 1/4W
4.7V
Zener diode 1N4732A, 1/4W; 47uF 25V, polarized; 5mm LED red, diffused
1)
PSpice 회로도
2)
230V 전원 전압파형
3) 230V
전원 전류파형
4)
230V 전원 전압×전류 파형
5)
Bride rectifier 입력 전압파형
6)
Bridge rectifier 출력 전압파형
7)
4.7μF 커패시터 전류파형
8)
22kΩ 전류파형
9)
10kΩ 전류파형
10)
Zener diode 전류파형
11)
Diode 전압파형
12)
Diode 전류파형
2. Constant-current LED driver with digital
control
- 아래 회로를 PSpice로 시뮬레이션 하라.
- LED를 위 그림에서와 같이 1.2Vdc 전원과 1N4002 다이오드의 직렬회로로 대체
- 동작원리:
T3: 입력 5V일 경우 LED OFF, 입력 0V일 경우 LED ON
Negative feedback: T2의 emitter에 전류가 흐르면 T1이 도통되어 2.2k 저항에 전류가 흐름. T1의 컬렉터 전류가 증가하면 T2의 베이스 전압이 감소하여 T1 컬렉터 전류의 증가를 억제 (negative feedback)

R = 39Ω, +V = 5V
그림: 디지털 제어가 가능한 LED 정전류 전원 회로 [Electro Schematics]
1) 회로도 제시
2)
T3 ON (입력에 5V 인가)일 경우 LED 전류
3)
T3 OFF (입력에 0V 인가)일 경우 LED 전류
4)
T3 OFF일 경우 T2 이미터 전압
II. 이론
1. 조명이론
1)
Solid angle (입체각)

그림: 입체각의 정의 [Wikipedia]
![]() : 입체각의 정의
: 입체각의 정의
A: 구면 중 입체각을 계산하고자 하는 면적
r : 구의 반경
![]()
- 입체각의 단위: steradian (sr)
- 구의 중심에서 구면 전체의 입체각은 4π
(sr)
- 참고: 원, 호의 길이, 평면각(radian)
![]()
- 부분 각도 입체각 계산
![]()
![]()
예: ![]()
![]()
2) 빛의 밝기
Radiant flux:
- 총 방사전력. radiant power. total radiated power. 광원이 전 각도로 방사하는 광 전력. 단위 Watt (W)
![]()
Spectral flux: spectral
power (density). power per frequency (or wavelength)
Luminous flux:
- 광전력. luminous power. The radiant flux adjusted to
reflect the varying sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of
light
![]() : lumen (lm), cd∙sr, candela over one steradian
: lumen (lm), cd∙sr, candela over one steradian
Luminous intensity:
- 휘도. 단위 입체각 당 광전력
Iv
:
candela, cd = lm/sr
1 cd = 1.46 mW/sr @ 555nm
(human eye is most sensitive to this wavelength)
- 촛불: 1cd
-
25W CFL:
1) 사방으로 방사: 1700 lm → I = 1700/4π = 135 cd
2) 20º로 방사 (방위각 2π),
Ω = 0.0955 sr → I =
1700/0.0955 = 17,800
-
LED: 전자회로용 50mcd, 초고휘도(ultra-bright) LED 15cd
Luminance:
- Used to characterize emission or reflection from
flat, diffuse surfaces.
Lv : cd/m2 (nit)
Illuminance:
- 단위면적 당 광전력
Ev : lux (lx), lm/m2
Luminous efficacy of radiation:
![]()
![]() : luminous flux (lm)
: luminous flux (lm)
![]() : radiant flux
: radiant flux
Luminous efficiency: lighting efficiency
Luminous flux (lm) divided power supplied power
(W)
2. 조명기술 비교
ㅇ 광원의 종류

- 백열등(incandescent light):
- Halogen(핼'러젼): "salt-producing". 불소 (F), 염소 (Cl), bromine (Br), astatine (At), tennessine
(Ts)의 총칭. 금속과 반응하여 여러 종류의 염(salt) 생성. calcium fluoride, sodium chloride, sliver
bromide, potassium iodide.
원소 자체는 독성이 있으며 접촉 시 치명적
표준 온도와 기압에서 고체, 액체, 기체 상태로 존재 가능
염소, 브롬, 요오드: 소독제, 살균제로 사용
Organobromide: 난연재료
Halogen 램프: 텅스텐 필라멘트, 소량의 요오드 또는 브롬. 핼러젼 원소를 채우지 않을 때보다 전구의 크기를 작게 할 수 있음.
ㅇ 광원의 특성비교
|
|
Incandescent power (W) |
Lumens |
LED |
CFL |
Fluorescent tube |
MH |
|
|
150 |
2600 |
|
30-52 |
|
|
|
|
100 |
1600 |
19-22 |
20-26 |
|
72 |
|
|
75 |
1100 |
15-20 |
16-23 |
|
53 |
|
|
60 |
800 |
10-12 |
13-15 |
|
43 |
|
|
40 |
450 |
5-9 |
10-11 |
|
29 |
|
Bulb cost($) |
1.25 |
|
35 |
4 |
|
|
|
Lifetime(hr) |
1,200 |
|
50,000 |
10,000 |
|
|
|
Lumens/W |
15 |
|
40-95 |
60 |
60-105 |
25 |
|
Color temp.(K) |
2700 |
|
2700- 6500 |
2700- 6500 |
3000- 6500 |
2700- 6500 |
ㅇ 광원별 광효율

그림: 조명기술 별 광효율 [.ST]
3. LED 조명
1) LED 기초
ㅇ LED 램프 효율
-
2017년 기준 LED 효율 (lm/W): http://donklipstein.com/led.html
Pure
red, deep red: 40
Orangish
red: 105
Red-orange:
150
Truly
orange: 102
Yellow
and amber: 110
Yellow-green:
140
Green:
125
Green,
InGaN: 165
Blue-green:
93
Blue:
39
White:
212
Warm
white: 150
ㅇ LED 효율/가격 전망치

그림: LED의 광효율과 가격 변화 추이 및 예측 [EIA]
ㅇ LED 전압-전류 특성


그림: Forward current vs forward voltage [Future
Electronics]


그림: Relative luminous intensity vs 1) forward
current and 2) ambient temperature [Future Electronics]

그림: Forward current vs ambient air temperature
[Future Electronics]


그림: 펄스 폭에 따른 최대 첨두 전류 [Future Electronics]
-
LED 전류계산

그림: LED 전류제한 저항 값 계산 [Electronics Stack Exchange]
![]()
ㅇ LED Color Chart [OK Solar]
|
|
Wavelength |
Color Name |
Fwd Voltage |
Intensity |
Viewing |
LED Dye Material |
|
|
940 |
Infrared |
1.5 |
16mW @ 50mA |
15° |
GaAIAs/GaAs |
|
880 |
Infrared |
1.7 |
18mW @ 50mA |
15° |
GaAIAs/GaAs |
|
|
|
850 |
Infrared |
1.7 |
26mW @ 50mA |
15° |
GaAIAs/GaAs |
|
|
660 |
Ultra Red |
1.8 |
2000mcd @ 50mA |
15° |
GaAIAs/GaAs |
|
|
635 |
High Eff. Red |
2.0 |
200mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
GaAsP/GaP |
|
|
633 |
Super Red |
2.2 |
3500mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
InGaAIP |
|
|
620 |
Super Orange |
2.2 |
4500mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
InGaAIP |
|
|
612 |
Super Orange |
2.2 |
6500mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
InGaAIP |
|
|
605 |
Orange |
2.1 |
160mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
GaAsP/GaP |
|
|
595 |
Super Yellow |
2.2 |
5500mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
InGaAIP |
|
|
592 |
Super Pure Yellow |
2.1 |
7000mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
InGaAIP |
|
|
585 |
Yellow |
2.1 |
100mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
GaAsP/GaP |
|
|
4500K |
"Incandescent" |
3.6 |
2000mcd @ 20mA |
20° |
SiC/GaN |
|
|
6500K |
Pale White |
3.6 |
4000mcd @ 20mA |
20° |
SiC/GaN |
|
|
8000K |
Cool White |
3.6 |
6000mcd @ 20mA |
20° |
SiC/GaN |
|
|
574 |
Super Lime Yellow |
2.4 |
1000mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
InGaAIP |
|
|
570 |
Super Lime Green |
2.0 |
1000mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
InGaAIP |
|
|
565 |
High Efficiency |
2.1 |
200mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
GaP/GaP |
|
|
560 |
Super Pure Green |
2.1 |
350mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
InGaAIP |
|
|
555 |
Pure Green |
2.1 |
80mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
GaP/GaP |
|
|
525 |
Aqua Green |
3.5 |
10,000mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
SiC/GaN |
|
|
505 |
Blue Green |
3.5 |
2000mcd @ 20mA |
45° |
SiC/GaN |
|
|
470 |
Super Blue |
3.6 |
3000mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
SiC/GaN |
|
|
430 |
Ultra Blue |
3.8 |
100mcd @ 20mA |
15° |
SiC/GaN |


ㅇ HB(high brightness) LED

그림: 고출력 LED 동작전류 및 동작전압 [RECOM]
2) LED 전원회로


그림: 1) 고휘도 LED 전원회로, 2) 구현된 회로. BR1: df04s, full bridge [IXYS]

그림: LED용 정전류 전원회로 [Electronics Stack Exchange]

그림: LED용 승압-정전류 전원회로 [Electronics Stack Exchange]. 정전류 공급. Vin 보다 다이오드 전압강하가 큰 경우 사용
ㅇ


그림: LED용 SEPIC 전원 회로 및 효율 [Electronics Stack Exchange]. 입력 DC 전압이 변동되는 경우 SEPIC 회로,
Buck-boot 회로, Cuk driver 회로 사용
3. HID 램프
ㅇ HID(high-intensity discharge) lamp
ㅇ 고휘도, 아크 방전, 텅스텐 전극, 가스/금속염(sodium or metal halide) 충전, 금속염 기화 플라즈마 생성, 가시광선 스펙트럼 분포율 높음, 자동차 전조등. 고효율. 장수명

그림: HID 램프의 구조
ㅇ 시동전압(ignition voltage, starting voltage)
- Probe start (standard
start)
- Pulse start: 3-5kV. hot
restrike voltage > 20kV
ㅇ 기술 사항
- 음파공진: acoustic resonance
-
Current/voltage waveform
-
Operating frequency: 0.1-1kHz
-
Flickering: fluctuation in light intensity
-
Warm-up phase: 2-5 min
-
Burn phase
-
ANSI lamp designation: 150W, 175W, 250W, 400W
-
Color temperature: each lamp has its own spectral signature
ㅇ Ballast
-
HID 램프 전원공급 장치: 시동전압, 동작전압/전류 생성 제어
- 아날로그 ballast
- 디지털

그림: HID electronic ballast 블럭도 [EDN]

그림: 250W HID 램프 전원용 ballast 회로 [ST]
- Booster
converter: 출력전압 제어, 역률개선(PFC)
-
Inverter stage: DC-AC current conversion
-
Synchronouse buck converter
-
Igniter block: high-voltage pulse
-
Square wave current for the lamp: duty cycle, charge-discharge cycle

그림: 1) HID 램프, 2) 전원장치 [ST Microelectronics]
4. 형광램프(FL)
5. 소형 형광램프(CFL)
6. 네온램프
III. 연습문제
1. 순방향 전압 2.0V에서 50mA가 흐르는 LED를 DC 5V 전원과 저항을 연결하여 동작시키고자 한다.
1) 저항값을 구하라.
2) 광효율(lighting efficiency)가 40%일 경우 radiant flux를 구하라.
3) 사방으로 균일하게 광을 방사할 경우 liminous intensity를 구하라.
4) 렌즈를 이용하여 중심축에서 30º 각도 이내로만 광을 방사할 경우 luminous intensity를 구하라.