Microwave
Engineering 01, Python Coding
1. Online study material
Tutorials
Point 'Learn Python': https://www.tutorialspoint.com/python/index.htm
2. Use Online Python
-
Access https://www.online-python.com/
- Copy or write down
your code in the upper window of 'Online Python'.
- Click [Run]
-
In the lower window, enter your data.
-
Program output will be displayed in the lower window.
![]()

-
To copy the text in the lower window, click [Stop], click the left top icon ![]()
- Go to your document,
then press Ctrl + V
(참고)
ㅇ
상단창(소스코드창) 상단에 배치된 아이콘
메뉴 의미
상단좌측
아이콘 4개: Open file From Disk, Save File to
Disk, Undo, Redo
상단우측
아이콘 3개: Change Theme, About Site,
Settings
ㅇ
하단창(입출력창) 좌측 아이콘 메뉴 5개의 의미
Copy
to clipboard: 출력창 내용을 클립보드에 copy (다음에 Ctrl+v로
문서에 삽입)
Download:
출력창 내용을 txt 파일로 컴퓨터로 다운로드
Clear:
출력창 내용 지움
Smart
terminal: >>>가 표시되고 interpreter 모드. Python를 1줄씩 실행. help(print)
와 같이 help 표시
Expand/Collapse:
Expand = 출력창만 전체화면에 표시, Collapse: 위창, 아래창 동시표시
3. 코딩실습
3.1 Example 1: Transmission
line. Calculate Z0, γ using R, L, G,
and C.
1) 문제
Input:
R, L, G, C of a transmission, f
Output:
Z0, γ
2) 수식
![]()
R
in ohm/m
L
in H/m
G
in S/m
C
in F/m
Z0
in ohm
Re(γ)
in Np/m
Im(γ)
in rad/m
3) 코딩
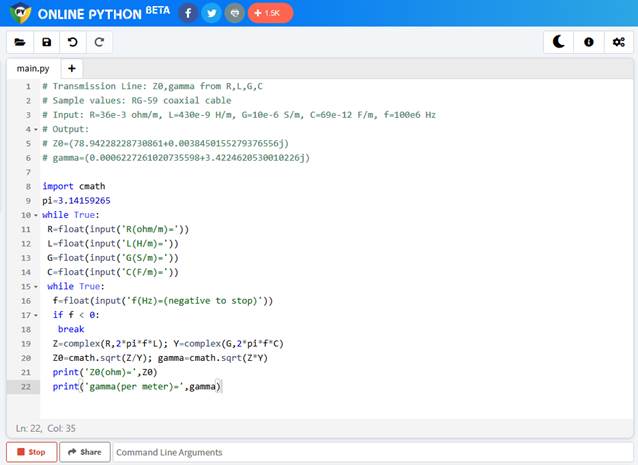
# MW-01-Python-Ex1
# Transmission Line: Z0, gamma from R, L,
G, C, f
# Sample values: RG-59 coaxial cable
# Input: R=36e-3 ohm/m, L=430e-9 H/m,
G=10e-6 S/m, C=69e-12 F/m, f=100e6 Hz
# Output:
# Z0=(78.94228228730861+0.0038450155279376556j)
#
gamma=(0.0006227261020735598+3.4224620530010226j)
import cmath
pi=3.14159265
while True:
R=float(input('R(ohm/m)='))
L=float(input('L(H/m)='))
G=float(input('G(S/m)='))
C=float(input('C(F/m)='))
while True:
f=float(input('f(Hz)=(negative to stop)'))
if f < 0:
break
Z=complex(R,2*pi*f*L); Y=complex(G,2*pi*f*C)
Z0=cmath.sqrt(Z/Y); gamma=cmath.sqrt(Z*Y)
print('Z0(ohm)=',Z0)
print('gamma(per meter)=',gamma)
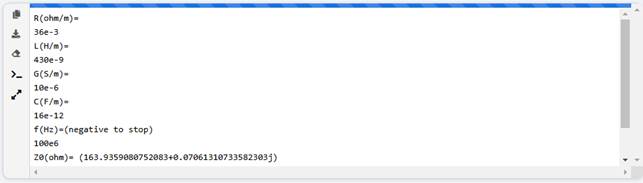
4) 코드 수행결과
R(ohm/m)=
36e-3
L(H/m)=
430e-9
G(S/m)=
10e-6
C(F/m)=
69e-12
f(Hz)=(negative
to stop)
100e6
Z0(ohm)=
(78.94228228730861+0.0038450155279376556j)
gamma(per
meter)= (0.0006227261020735598+3.4224620530010226j)
f(Hz)=(negative
to stop)** Process Stopped **
Press
Enter to exit terminal
3.2 Example 2: Transmission
line. Calculate R, L, G, and C from Z0 and γ
1) 문제
Input:
Z0, γ
Output:
R, L, G, C
2) 수식
![]()
3) 코딩
#
EM-01-Python-Ex2: R, L, G, C from Z0, γ and f
#
Input: Z0 = 79 + 3.8e-3j, gamma=6.2e-4+3.4j, f=100e6
#
Output:
import cmath
pi=3.14159265
while True:
Z0=complex(input('Z0(ohm)='))
gamma=complex(input('gamma(per meter)='))
f=float(input('f(Hz)='))
w=2*pi*f
temp=gamma*Z0 ; R=temp.real ; L=temp.imag/w
temp=gamma/Z0 ; G=temp.real ; C=temp.imag/w
print('R(ohm/m)=',R)
print('L(H/m)=',L)
print('G(S/m)=',G)
print('C(F/m)=',F)
4) 코드 수행결과
Z0(ohm)=
79+3.8e-3j
gamma(per
meter)=
6.2e-4+3.4j
f(Hz)=
100e6
R(ohm/m)=
0.03606
L(H/m)=
4.27490181383e-07
G(S/m)=
9.918282303601987e-06
C(F/m)=
6.849706343446908e-11
Z0(ohm)=**
Process Stopped **
Press
Enter to exit terminal
3.3 Example 3: 복소수 계산
(참고) Python에서 복소수 연산
ㅇ 표기: 1+2j, 1.+1.j, 2j
ㅇ 입력시 괄호 없이 1+2j와 같이 입력
ㅇ 출력시 괄호가 사용됨 (실수, 허수 모두 있을 때)
2j
(1+2j)
ㅇ 실수부와 허수부는 실수 규칙을 따름.
ㅇ 복소수 지정
z=3+2j
z=complex(3,2)
ㅇ 복소수 연산
4칙연산: + - * / **
z1+z2, z1-z2, z1*z2, z1/z2
z1**2, pow(z, 2), z1**z2
z.real
z.imag
z.conjugate()
z=complex(x, y)
z=complex(2, 4)
z=complex(2) # z=2+0j
ㅇ 복소수 라이브러리 함수
from cmath import *
polar(z): a tuple value
zm=polar(z)
zm[0] : mag(z)
zm[1] : phase(z)
rect(r, phi) : a complex value
exp(z), phase(z), abs(z), log(z,
[base]), log10(z), sqrt(z)
acos(z), asin(z), atan(z), cos(z),
sin(z), tan(z)
acosh(z), asinh(z), atanh(z),
cosh(z), sinh(z), tanh(z)
ㅇ Tuple: 항목값 변경 불가, 변경가능한 것은 list
t1 =
()
t2 =
(1,)
t3 =
(1, 2, 3)
t3[0]
# t3의 첫번째값 1
len(t3)
# t3의 요소수 4
t3*3
t4 = 4,
5, 6
t3+t4
# (1,2,3,4,5,6)
t5 =
('a', 'b', ('ab', 'cd'))
t6=t3+t4
t6[1:4]
# (2,3,4,5)
t6[1:]
# (2,4,4,5,6)
t6[:4]
# (1,2,3,4,5)
1) 문제
복소수 z1과 z2를 입력받아 z3 = z1*z2, z4=z1/z2를 실수/허수, 크기/위상(radian)으로 표시
2) 수식

3) 코딩
# MW-01-Python-Ex3: Complex
calulation
from cmath import * # Use the complex
math library in Python
while True:
z1=complex(input('z1='))
z2=complex(input('z2='))
z3=z1*z2; z4=z1/z2
zp3=polar(z3); zp4=polar(z4)
z3arg=zp3[1]*180/3.14159
z4arg=zp4[1]*180/3.14159
print('z3=',z3,'z3(polar)=',zp3,'arg(z3)(deg)=',z3arg)
print('z4=',z4, 'z4(polar)=',zp4,'arg(z4)(deg)=',z4arg)
4) 코드 수행결과
z1=
1+2j
z2=
3+4j
z3= (-5+10j) , z3(polar)= (11.180339887498949, 2.0344439357957027) , arg(z3)(deg)= 116.56514963544781
z4= (0.44+0.08j) , z4(polar)= (0.4472135954999579, 0.17985349979247828) , arg(z4)(deg)= 10.304855172904833
z1=** Process Stopped **
Press Enter to exit terminal
3.4 Example 4: R, L, C
serie circuit impedance
1) 문제
R, L, C, f 가 주어진 경우 RLC 직렬회로와 RLC 병렬회로의 임피던스를 계산하라.
2) 수식

R in Ω (Ohm)
L in H (Henry)
C in F (Farad)
ω in rad/s
f in Hz (Herz)
3) 코딩
#
MW-01-Python-Ex4: RLC series and parallel circuits
pi=3.141593
while
True:
R=float(input('R(ohm)='))
L=float(input('L(uH)='))
C=float(input('C(uF)='))
f=float(input('f(Hz)='))
w=2*pi*f
Zs=complex(R, w*L*1e-6-1/(w*C*1e-6))
Zp=1/complex(1/R, w*C*1e-6-1/(w*L*1e-6))
print('Z(series)=', Zs)
print('Z(parallel)=', Zp)
4) 코드 수행결과
R(ohm)=
100
L(uH)=
20
C(uF)=
50
f(Hz)=
1e6
Z(series)=
(100+125.66053690148915j)
Z(parallel)=
(1.0132629437904996e-07-0.0031831791384774404j)
R(ohm)=**
Process Stopped **
Press
Enter to exit terminal