GNSS - Fast Acquisition with Low Signal Level
[GPS Receiver Start-Up and Operational Modes]
• Receiver operational modes: cold start, warm start, hot start, reacquisition, assisted GPS, self-assisted GPS, DGPS
[Factory Start]
• Receiver never used since fabrication
• Receiver not powered for more than a year.
• No information at all on GPS satellite. The GPS receiver chip has never been fully operated after its semiconductor fabrication.
• Almanac download alone takes 12.5 minutes.
• TTFF = 13.5 min.
[Cold Start]
• Receiver not
powered for 8-12 hours.
• Almanac in non-volatile memory is valid.
• Invalid ephemeris (older than 4 hours): ephemeris data is broadcast every 30 seconds.
• Receiver position not valid: away from previous fix by more than 100km
• Receiver time: unknown
• Receiver works through an internal list of all satellites acquiring each SV in view in turn. Acquisition time is the longest among all start-up modes.
• TTFF = 30-40s @ 2011
• Forced cold start: wrong information (very old almanac) on SV will make receiver spend more time than in the total cold start mode. In this case, a forced cold start is necessary.
[Warm Start]
• Receiver not powered for 30 minutes.
• Valid almanac
• Invalid ephemeris (older than 4 hours)
• Receiver position: approximately known (within 100km of the last fix)
• Receiver time: approximately known (GPS has been active in the last three days or RTC has been on by backup power).
• Receiver immediately detects overhead SVs but needs to download current ephemeris data.
• TTFF = 30-40s @ 2011 (not much different from cold-stat time)
[Hot Start]
• Receiver not powered for 15 minutes.
• Valid almanac
• Valid ephemeris data for at least 5 SVs (less than 4 hours old)
• Receiver position: not changed (exactly known)
• Receiver time: exactly known
• Receiver rapidly tracks overhead SVs and needs to download a minimum of data.
• TTFF = 1s @ 2011
[Reacquisition]
• Receiver always being powered. After blockage for up to 10s while tracking SV signals.
• TTFF < 1s @ 2011
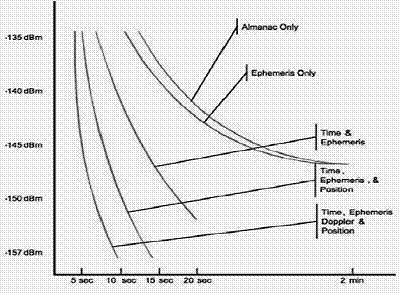
[Assisted GPS(AGPS)]
• Receiver always being powered and assistance data always received.
• Relay information (= assistance data) to GPS receiver to help shorten acquisition time.
- SV ephemeris (orbit parameters): mandatory
- SV clock corrections: mandatory
- Other error corrections: ionospheric, tropospheric
- Accurate local time: produces 3dB sensitivity improvement
- GPS receiver (UE=user equipment) location
- Visible satellites
- Relative code delay offsets
- Doppler frequencies
- DGPS corrections (optional)
- Navigation message bits: produces 3dB SNR improvement
• GPS receiver maximum distance from server station: 150km
• Benefits:
- Search space is drastically reduced.
100-1000 times faster in all SNR conditions
- SNR (code phase tracking) improvement: 25dB, operation in low signal and heavy multipath environments (foliage, indoors, urban canyons).
- TTFF almost independent of SNR.
- Indoor operation
of GPS is possible.
-
Accuracy: 4m
open sky, 20-50m(indoors, urban canyons)
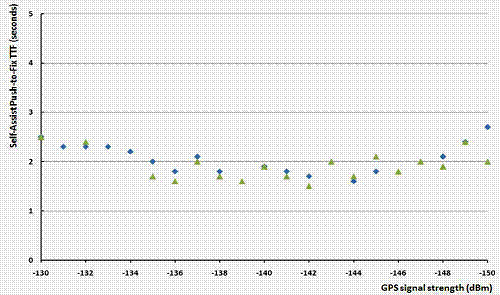
[Self-Assisted GPS]
• Receiver did not work for last 4 hours -> Warm stat when re-powered.
• Extend this 4-hr limit by precisely predict (based on planetary physics) the SV trajectory from the last ephemeris data up to 3 days (72 hours).
• TTFF = 3s @ 2011